Free Shipping in the U.S. for orders over $1000. Shop Now>>

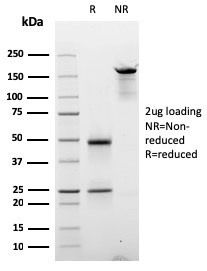
Cyclin E is a regulatory protein involved in cell cycle progression, particularly in the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase. It is encoded by the CCNE1 gene, located on chromosome 19q12 in humans. Cyclin E contains 400 amino acids with a molecular weight of around 50 kDa. Post-translational modifications of cyclin E include phosphorylation, which regulates its activity during different phases of the cell cycle. Cyclin E is primarily an intracellular protein, functioning as a regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2). Together, cyclin E and CDK2 form an active complex that phosphorylates target proteins, promoting the initiation of DNA replication and progression through the cell cycle. This protein is expressed in various tissues and cell types, with particularly high levels observed in proliferating cells.
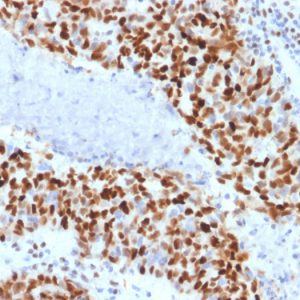
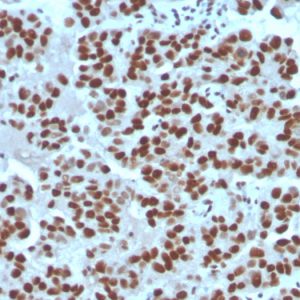
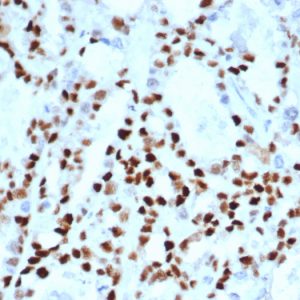
Notably, mutations in cyclin E or its dysregulated expression have been shown to impair cell cycle control and contribute to tumorigenesis. Overexpression of cyclin E has been observed in a wide range of human cancers, including breast, ovarian, lung, and colorectal cancers, leading to increased cell proliferation, genomic instability, and tumor progression. In some cancer types, upregulated cyclin E expression has been associated with more aggressive tumor phenotypes and poorer prognosis, making it a potential prognostic marker for cancer aggressiveness and patient outcomes. In this sense, monitoring cyclin E expression analysis may provide valuable diagnostic and prognostic information in cancer management,
Given its role in promoting cell proliferation and tumorigenesis, cyclin E has been investigated as a therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Strategies aimed at inhibiting cyclin E activity or expression, such as small molecule inhibitors or gene silencing approaches, have been explored for their potential to halt tumor growth and induce cancer cell death. Targeted therapies directed against cyclin E-overexpressing tumors may offer a personalized treatment approach for patients with cyclin E-driven cancers. While there are ongoing efforts to develop cyclin E-targeted therapies, further research is needed to validate their efficacy and safety in clinical settings. Immunotherapy approaches targeting cyclin E-expressing cancer cells may offer alternative strategies for cancer treatment, although specific examples of immunotherapy targeting cyclin E remain to be reported.
NeoBiotechnologies offers a variety of antibodies against cyclin E that have been validated for ELISA, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting. Additionally, we hold exclusive rights to cyclin E antibodies available for licensing or collaboration [https://www.neobiotechnologies.com/shop/?s=cyclin+e].
G1/S-specific cyclin-E1, CCNE1; Cyclin E1; G1/S-specific cyclin-E1
Cardiovascular, Infectious Disease, Lung Cancer, Nuclear Marker, Signal Transduction, Transcription Factors
Showing all 5 results

Showing all 5 results

Notifications